What is Scoliosis?
The name Scoliosis comes from a Greek word which means crooked. Scoliosis can be described as a disorder which causes an abnormal curve of the spine or backbone. The curvature can bend towards the right or left, and can be in the spine’s upper part (a thoracic curve), in the spine’s lower part (a lumbar curve), or can go from the lower to the upper part of the spine (known as, thoraco-lumbar curve). In certain cases, there can be a double curve like an S shape.
Scoliosis can affect your appearance because when your spine bends on the sides, the bones which make up the spine (known as vertebrae) can get twisted. A twisted vertebrae may pull your ribs around with them, which can cause a lump to form up on your back and can even adversely affect how your lungs work.
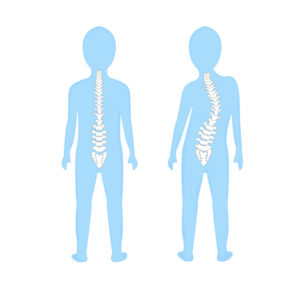
Types of Scoliosis
Congenital: This is where the small bones in the spine don’t form correctly before birth.
Neuromuscular: This type of scoliosis is related to issues with the muscles and the nervous system, including muscular dystrophy, cerebral palsy and spina bifida.
Idiopathic: This type develops in perfectly healthy children who have otherwise healthy bones; the reason for this type of scoliosis to develop is still unknown. It is the most common type, and accounts for about 8 out of every 10 cases.
Mechanical: This type of scoliosis makes it appear like a child has scoliosis, whereas in actual sense he/she doesn’t; 1 leg is usually much longer than the other.
Adult scoliosis: Scoliosis is fairly uncommon in adults. In adults, scoliosis can be caused by degenerative joint problems. In most situations, the scoliosis may have started in childhood, but wasn’t diagnosed until later in life.
Causes of Scoliosis
- Uneven leg length: Having 1 leg which is longer than the other can cause the hips to tilt. In order to compensate, the shoulders will tilt the other way.
- Neuromuscular conditions: Some conditions like cerebral palsy can make the muscle spasm which in turn pulls the vertebrae out of its natural alignment.
- Some diseases such as osteoarthritis can also cause this condition.
- Genetic factors: In certain cases, scoliosis tends to run in families.
- Congenital abnormalities: Some children might be born with structure defects like in the spinal cord and brain stem. Such defects might contribute to the development of scoliosis.
- Bad posture.
- Regular use of heavy backpacks and/or satchels.
- Improper exercise may also cause scoliosis.
Signs and Symptoms of Scoliosis
Scoliosis can be severe, moderate or mild. The signs and symptoms include, but are not limited to;
- A visibly curved spine.
- One shoulder tilting downwards towards a raised hip, as if leaning sideways.
- Ribs are more prominent.
- Protruding shoulder blade.
- Tilted waist.
- The curve is much more pronounced when you bend forward.
- Clothes not hanging as they should.
- Asymmetric location or size of breast (in females).
- The head isn’t centered directly above the pelvis.
- The entire body leans to one side.
- Unequal distances between the arms and the body.
- Rib cages which have different heights.
- Visible difference in the texture and look of skin which is overlying on the sides of the spine.
